How to transfer heat
There are three types of heat transfer.
1Heat conduction
A phenomenon in which heat is transferred directly from the other party by touching an object is called heat conduction. If you touch the handle of the wok directly, it will feel so hot that you will burn yourself.
The way of heat transfer varies depending on the object. The ladle of the Chinese ladle is very hot and not touched with bare hands, but I think it will be touched with the plastic handle.
This is due to the inherent thermal conductivity of the material. The higher the thermal conductivity, the easier it is to transfer heat.
2Heat transfer
Heat transfer is a phenomenon whereby air conducts heat even if it does not directly touch an object. Direct contact (heat conduction) with the flame by a fire can cause burns, but if it hits the flame at a certain distance, it will cause it to warm up. This phenomenon is called heat transfer, in which the air is heated by an open-air fire and the air feels warm because it transmits heat to people (the “wind blows up the tub”).
3Radiation
This phenomenon, in which heat is transferred neither to the object nor to the air, is called radiation. In our familiar case, the heat from the sun reaches us on the earth. Because of the vacuum between the sun and Earth in space, there is no gas for heat transfer. Even so, the heat from the sun is transmitted. This is because objects always emit energy (electromagnetic waves, which are difficult to say), which does not affect the distance or the medium but can reach the other party directly. This phenomenon is called radiation.
Melting temperature of metal
Top 10 Metal Heat Resistance Ranking !
- Tungsten (W):3407°C
- Rhenium (Re):3180°C
- Osmium (Os):3045°C
- Tantalum(Ta) :2985°C
- Molybdenum (Mo) :2623°C)
- Niobium(Nb) :2477°C
- Iridium (Ir) :2443°C
- Ruthenium(Ru) :2250°C
- Hafnium (Hf) :2233°C
- Technetium(Tc) :2157°C




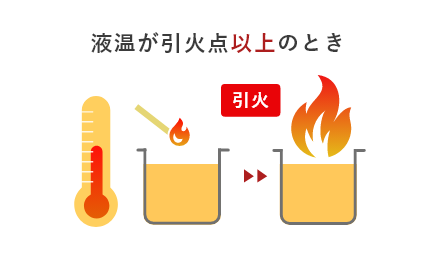
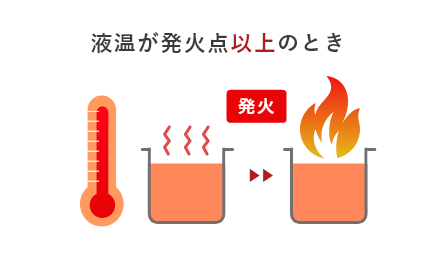


The metal with the highest melting temperature is tungsten!
All BEST 3 materials exceed 3000°C.
Tungsten and rhenium in rankings 1 and 2 are the component materials of C thermocouples.