Knowledge
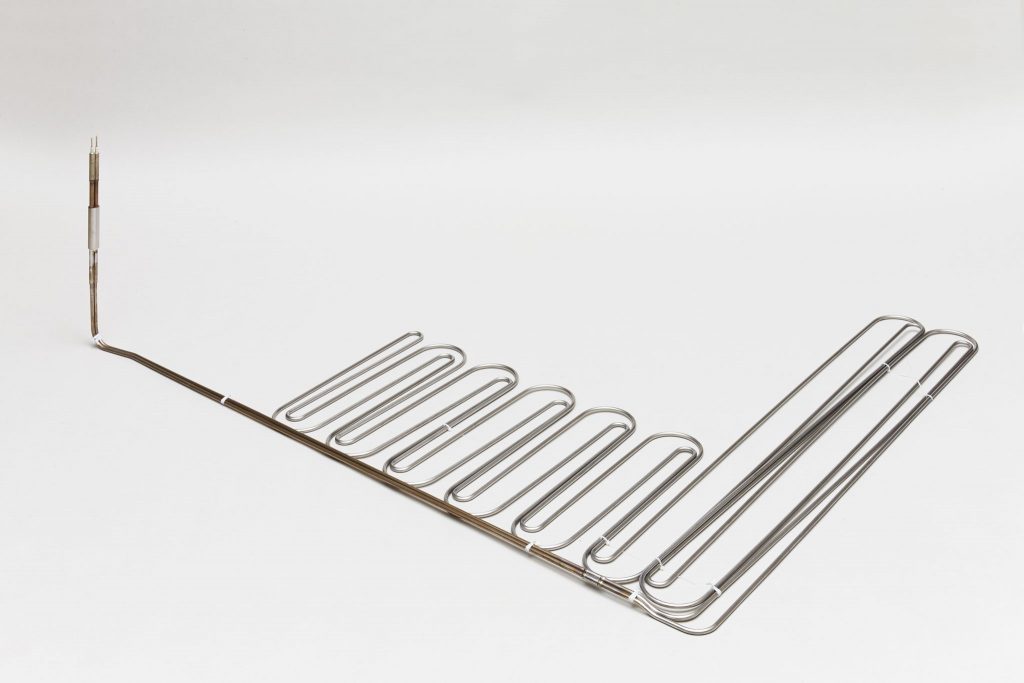
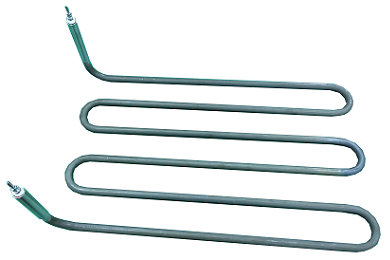
Electric heater
What is an electric heater?
Electric heaters include resistance heating, induction heating, and arc heating. By using a heating method that takes advantage of the advantages of the heating purpose, it is possible to efficiently heat the whole heating, surface heating, partial heating, etc., at an accurate temperature and the required time. A resistance heater heats an object to be heated by radiation, convection, or conduction of heat generated through an electric current through a resistance conductor (heating element) that can withstand high temperatures.
The electric heating heater introduced here is a resistance heating heater in which a metal resistance wire is covered with an insulating material and further covered with a metal tube or metal plate.
Features of electric heater
Electrothermal heaters used in industrial applications have the following features:
- Thermal efficiency is greater than that of the combustion system.
- Does not generate hazardous byproducts or waste.
- Homogeneous heating is easy.
- Easy handling and operation.
- Heating in high temperature and vacuum is possible.
- Easy temperature control.
- Easy automatic and remote control.
Components of the heating wire
Than JIS C 2520
| Type Symbol |
Chemical composition(%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(*1) | Cr | Al | C | Si | Mn | Fe(*2) | |
| Nickel chromium wire type 1 for electric heating NCHW1 |
77 or more | 19 ~ 21 | – | 0.15 Below | 0.75 ~ 1.6 | 2.5 Below | 1.0 Below |
| Nickel chromium wire type 2 for electric heating NCHW2 |
57 or more | 15 ~ 18 | – | 0.15 Below | 0.75 ~ 1.6 | 1.5 Below | Remainder |
| Class 3 nickel chromium wire for electric heating NCHW3 |
34 ~ 37 | 18 ~ 21 | – | 0.15 Below | 1.0 ~ 3.0 | 1.0 Below | Remainder |
| Class 1 chromium wire for electric heating FCHW1 |
– | 23 ~ 26 | 4 ~ 6 | 0.10 Below | 1.5 Below | 1.0 Below | Remainder |
| Type 2 chromium wire for electric heating FCHW2 |
– | 17 ~ 21 | 2 ~ 4 | 0.10 Below | 1.5 Below | 1.0 Below | Remainder |
(*1) The nickel may contain a small amount of cobalt.
(*2) Other elements may be included.
Maximum operating temperature and volume resistivity of heating wire
From JIS C 2520
| Type | Heating element surface Upper category temperature(℃) |
Volume resistivity(at23℃:μΩm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard value | Tolerance | ||
| Nickel chromium wire type 1 for electric heating | About 1100 | 1.08 | ±0.05 |
| Nickel chromium wire type 2 for electric heating | About 1000 | 1.12 | ±0.05 |
| Class 3 nickel chromium wire for electric heating | About 800 | 1.01 | ±0.05 |
| Class 1 chromium wire for electric heating | About 1250 | 1.42 | ±0.06 |
| Type 2 chromium wire for electric heating | About 1100 | 1.23 | ±0.06 |
The maximum operating temperature of the heating wire is related to the diameter of the heating wire. The maximum operating temperature decreases as the diameter becomes smaller. The maximum operating temperatures shown in the table above are for reference purposes only and their service life is not guaranteed.